Australia and Oceania is the name for the union of the island world of Oceania and Australia into one continent.
Geography
Australia and Oceania comprise the main land mass of the country of Australia itself, offshore New Zealand in the southeast as well as the entire South Pacific region with the large island regions of Melanesia (including New Guinea), Micronesia and Polynesia. The over 7,500 islands together cover a land area of almost 1.3 million square kilometers and extend over a marine area of approximately 70 million square kilometers. The state of Australia has a land area of 8 million km².
According to Countryaah – which mentions country facts – the continent of Australia consists only of the state of Australia and the offshore islands of Tasmania and New Guinea; the island world of Oceania is therefore not attributed to Australia.
Climate and vegetation
The continent of Australia itself spans three climate zones. While the interior of Australia is extremely dry and there are extensive desert areas, the coasts of Australia are tropical or subtropical. There is very little rainfall on large parts of the west and south coast. Due to the different climatic regions, Australia has very different types of landscape. There are tropical rainforests, various types of savannas and deserts.
The animal world is unique because marsupials (kangaroo, koala) and cloak animals like the platypus live in Australia. The bird life is particularly diverse. Bird species are extremely rare on New Zealand and many islands in Oceania. The European settlers introduced dogs, cats, rats and rabbits, which reproduce extremely strongly; this is why many of the native animal species are now at great risk. The colorful flora of Australia and Oceania is just as diverse as the animal world. The sea is an important habitat: there are many fish and aquatic plants, especially near the coral reefs off the coasts of Australia and the islands.
| Country | Average temperature / day |
| Australia | Canberra 6 ° C (July), 20 ° C (Jan) |
| Fiji | 27 ° C (Jan), 23 ° C (July) |
| Kiribati | about 28 ° C all year round |
| Marshall Islands | 27 ° C |
| Micronesia Federation | 26–29 ° C all year round |
| Nauru | 28 ° C all year round |
| New Zealand | Auckland 19 ° C (Jan), 11 ° C (July), Christchurch 17 ° C (Jan), 6 ° C (July) |
| Palau | Koror 27 ° C |
| Papua New Guinea | Port Moresby 26 ° C (July), 28 ° C (Dec) |
| Solomon Islands | Honiara 27 ° C |
| Samoa | 23–30 ° C all year round |
| Tonga | Tongatapu 21 ° C (July), 25 ° C (Jan) |
| Tuvalu | about 29 ° C all year round |
| Vanuatu | Port Vila 22-27 ° C |
Population
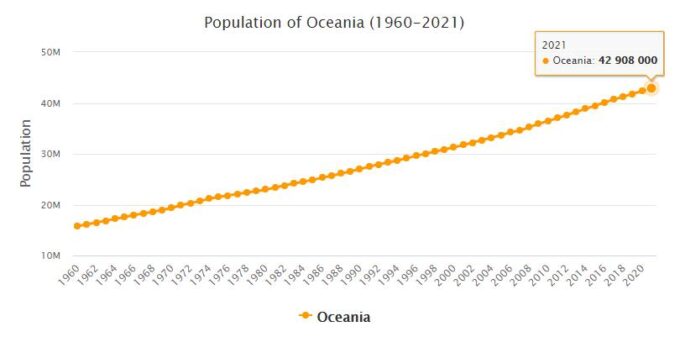
A total of 33 million people live in Australia and Oceania, well below one percent of the earth’s population. Above all people of European descent (mostly English or Irish) live in Australia, indigenous peoples like the Melanesians, Micronesians and Polynesians in the South Pacific. The aborigines of Australia, the indigenous Aborigines, make up a negligible proportion of the population of Australia. Much of the population of this continent belongs to the Christian faith. To see population of all capitals in Oceania and Australia, please visit AllCityCodes.
Plant life in Australia
Plant life is very varied and much of it is unique to Australia. Some genera are of a primitive type that exist only as fossils in other parts of the world. The vegetation indicates that Australia has previously had a land link with South Africa. The northern part of Queensland has a certain element of Malay forms. Vegetation varies with rainfall. The most precipitous areas are wooded. Forests grow in a belt along the entire east coast, all the way to the western foothills of the Great Dividing Range. In the northeastern part of Queensland there are some areas with species rich tropical rainforest. The rest of the east coast down to the Bass Strait, as well as Tasmania, has subtropical rainforest. In this forest, different species of eucalyptus dominate.
In southeastern Australia, huge forests of giant eucalyptus trees (Eucalyptus amygdalina) grow, with dense undergrowth. The coastal plain itself on the east coast is drier than the mountainous areas, and here it is savanna or glitzy savanna forest. The southwest corner of Western Australia has dense subtropical forest. Here, 60-70 m tall curry trees (Eucalyptus diversicolor) grow with an undergrowth of palm trees and shrubs. In a narrow belt on the western slope of the inland plateau, the forest consists of jarrah trees (Eucalyptus marginata). In a wide belt along the north coast there is forest water, and in some areas there are denser forests of eucalyptus and palm trees. Where the annual rainfall falls below 500 mm, the forest ends and the vegetation changes to savanna and steppe.
Areas with an annual rainfall of less than 250 mm are desert-like, where bushes of different acacia species dominate. When it rarely rains, a carpet of annuals appears. Areas with an annual rainfall of less than 125 mm are desert with sand dunes and sand plains. The vegetation consists mostly of different grasses with hard, prickly leaves. Large areas are salt steppe, where various halophilic plants (salt plants) grow. The Australian vegetation consists of an unusual number of endemic (native) species. As an example, the Eucalyptus tree genus consists of more than 500 species, of which only 2 or 3 are found outside Australia.
Guam
At the beginning of 1998, the island relied on middle-class tourism, which consisted mainly of tourists from Japan, South Korea and Taiwan. These tourists left about $ 300 million in the country per year. season. Governor Gutiérrez wanted to increase this figure 50% over the following 5 years. The number of tourists in 2000 exceeded 1 million.
On December 8, 2002, the typhoon hit Pongsona Island, destroying communications links and many houses and trees. 4 people were killed and 400 injured.
Guam suffered major losses during World War II and in 2003 set up an investigative committee to carry out investigations into the events of the war until June 2004. It received 70 testimonies from survivors of the war that would serve to build the arguments that the United States should treat the country in the same way as other territories such as the Philippines and Micronesia, which received compensation for the Japanese occupation during the World War.
In February 2004, a United States Air Force spokeswoman stated that six more B-52 bombers and 300 soldiers would be sent to the island to reinforce existing force and to increase pressure on North Korea.
Erosion in the country has doubled over the past 30 years. The main cause is the destruction of forests ifbm. the construction of roads. Guam loses an average of 243 tons of soil per day. acre pr. year.
During his speech to the nation in February 2010, Governor Felix Camacho declared that the country’s name should be changed to the Chamoros’ version of Guam: Guahan. This name was widely used about the country during the period 1521-1898, and the governor issued a directive on the same day confirming the change of name. It was the United States that in 1900 christened the country of Guam. Felix Camacho has already sat for two terms and therefore cannot be re-elected when his term expires in 2011. The name change is a way to put his fingerprint on the country’s history, he has publicly admitted..
In preparation for future military conflicts with China, in 2010-14, the United States conducted a gigantic expansion of its military bases on the island. The construction workers temporarily increased the country’s population by 40% or 80,000 people. In 2010, US military bases accounted for 29% of the country’s total area. It grew to 40% in 2014. It was planned that the transfer of marines and their relatives from the US base in Okinawa should begin as early as 2010. 8,000 soldiers will be transferred as well as 9,100 relatives. However, plans were slowed as the islands did not have enough fresh water to meet the needs of the soldiers. The superpower base in Okinawa was facing increasingly harsh criticism from the Japanese population as many young Japanese women were subjected to rape by the soldiers.
In late summer 2017, the United States and North Korea escalated the reciprocal security policy situation in the wake of North Korea’s development of nuclear weapons and intercontinental missiles and an escalation of US military and political threats to the country. In August, North Korea threatened to launch medium-range missiles against Guam, which would land in the sea 20-40 km from the island, serving as an advanced military base for the United States.